CHAPTER 2: IDENTIFYING COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE
MGT300
Chapter 2: Identifying Competitive Advantage
- Explain why competitive advantages are typically temporary.
- List and explain each of the five forces in Porter's Five Forces Model.
- Compare Porter's three generic strategies.
- Describe the relationship between business processes and value chain.
What is competitive advantage?
- A product or service that an organization's customers place a greater value on than similar offerings from a competitor.
- Unfortunately, CA is temporary because competitors keep duplicate the strategy.
- The, the company should start the new competitive advantage.
FIVE FORCES MODEL
- Buyer Power:
- High- when buyers have many choices of whom to buy
- Low- when their choices are few.
- To reduce buyer power (and create competitive advantage), an organization must make it more attractive to buy from the company not from the competitors.
- Best practices of IT-based
- Supplier Power
- High- when buyers have few choices of whom to buy from.
- Low- when their choices are many.
- Threat of Substitute Product & Services
- High- when there are many alternatives to a product or service.
- Low- when there are few alternatives from which to choose.
- Ideally, an organization would like to be on a market in which there are few substitutes of their product or services.
- Thereat of New Entrants
- High- when it is easy for new competitors to enter a market
- Low- when there are significant entry barriers to entering a market
- Entry barriers is a product or service feature that customers have come to expect from organizations and must be offered by entering organization to compete and survive.
- Best practices of IT
- Rivalry Among Existence Competitors
- High- when competition is fierce in a market
- Low- when competition is more complacent
- Best Practices of IT
THE THREE GENERICS STRATEGIES
- Cost Leadership
- Becoming a low-cost producer in the industry allows the company to lower prices to customers
- competitors with higher costs cannot afford to compete with the low-cost leader on price
- Differention
- Create competitive advantage by distinguishing their products on one or more features important to their customers.
- Unique feature or benefits may justify price differences and/or stimulate demand
- Focused Strategy
- Target to a niche market
- Concentrates on either cost leadership or differentiation
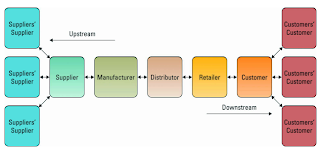
The Value Chains- Targeting Business Processes
- Supply Chain- a chain or series of processes that adds value to product & service for customer.
- Add value to its products and services that support a profit margin for the firm.
26/9/2017
TUESDAY
Comments
Post a Comment