CHAPTER 14: CREATING COLLABORATIVE PARTNERSHIPS
Creating Collaborative Partnerships
Teams, Partnerships, and Alliances:
- organizations create and use teams, partnerships, and alliances to:
- undertake new initiatives
- address both minor and major problems
- capitalize on significant opportunities
- organizations create teams, partnerships, and alliances both internally with employees and externally with other organizations
- collaboration system- supports the work of teams by facilitating the sharing and flow of information.
- organizations from alliances and partnerships with other organizations based on their core competency
- core competency- an organization's key strength, a business function that it does better than any of its competitors
- core competency strategy- organization chooses to focus specifically on its core competency and forms partnerships with other organizations to handle nonstrategic business processes
- information technology can make a business partnership easier to establish and manage
- information partnership- occurs when two or more organizations cooperate by integrating their IT systems, thereby providing customers with the best of what each can other
- the internet has dramatically increased the ease and availability for IT-enabled organizational alliances and partnerships
Collaboration Systems:
- collaboration solves specific business tasks such as telecommuting, online meetings, deploying applications, and remote project and sales management
- Collaboration system- an IT-based set of tools that supports the work of teams by facilitating the sharing and flow of information
- two categories of collaboration
- unstructured collaboration (information collaboration) - includes document exchanges, shared whiteboards, discussion forums, and e-mail
- structured collaboration (process collaboration) - involves shared participation in business processes such as workflow in which knowledge is hardcoded as rules
- collaborative business functions
- collaboration systems include:
- knowledge management systems
- content management systems
- workflow management systems
- groupware systems
Knowledge Management Systems:
- knowledge management (KM) - involves capturing, classifying, evaluating, retrieving, and sharing information assets in a way that provides context for effective decisions and actions
- knowledge management system - supports the capturing and use of an organization's "know-how"
- intellectual and knowledge-based assets fall into two categories
- explicit knowledge - consists of anything that can be documented, archived, and codified, often with the help of IT
- tacit knowledge - knowledge contained in people's heads
Explicit and Tacit knowledge:
- the following are two best practices for transferring or recreating tacit knowledge
- shadowing - less experienced staff observe more experienced staff to learn how their more experienced counterparts approach their work
- joint problem solving - a novice and expert work together on a project
- reasons why organizations launch knowledge management programs

KM Technologies:
- knowledge management systems include:
- knowledge repositories (databases)
- expertise tools
- e-learning applications
- discussion and chat technologies
- search and data mining tools
KM and Social Networking:
- finding out how information flows through an organization
- social networking analysis (SNA) - a process of mapping a group's contacts (whether personal or professional) to identify who knows whom and who works with whom
- SNA provides a clear picture of how employees and divisions work together and can help identify key experts
Content Management:
- content management system (CMS) - provides tools to manage the creation, storage, editing, and publication of information in a collaborative environment
- CMS marketplaces includes:
- Document management system (DMS)
- Digital asset management system (DAM)
- Web content management system (WCM)
- content management system vendor overview
Working Wikis:
- Wikis - web-based tools that make it easy for users to add, remove, and change online content
- Business wikis - collaborative web pages that allow users to edit documents, share ideas, or monitor the status of a project
Workflow Management Systems:
- work activities can be performed in series or in parallel that involves people and automated computer systems
- workflow - defines all the steps or business rules, from beginning to end, required for a business process
- workflow management system - facilitates the automation and management of business processes and controls the movement of work through the business process
- messaging-based workflow system - send work assignments through an e-mail system
- database-based workflow system - stores documents in a central location and automatically asks the team members to access the document when it is their turn edit the document
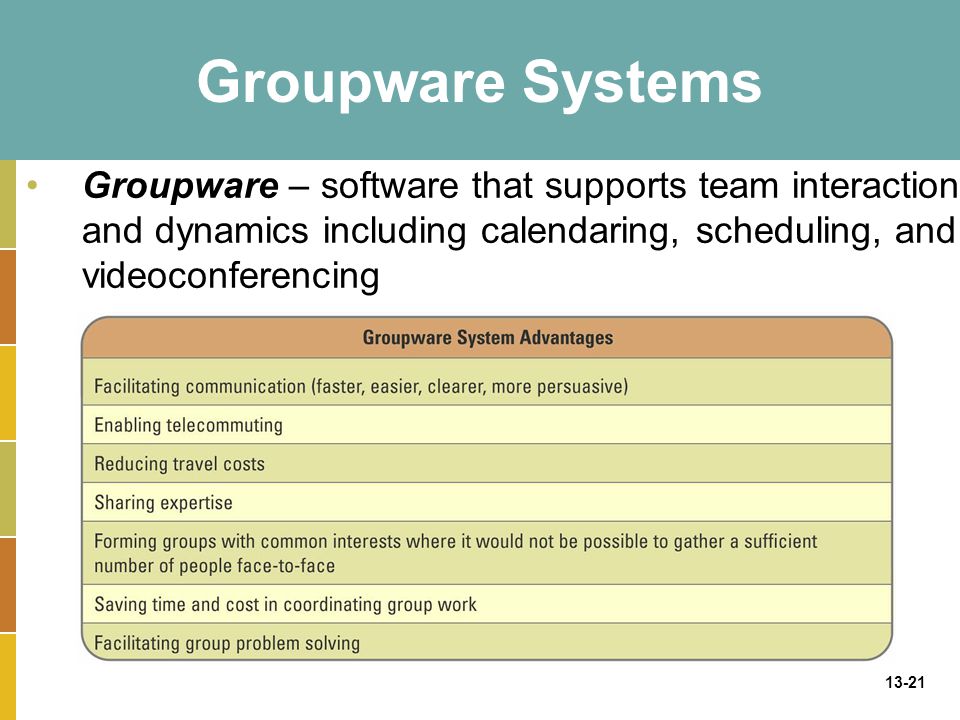
Groupware Systems:
- groupware technologies

Videoconferencing:
- videoconference - a set of interactive telecommunication technologies that allow two or more locations to interact via two-way video and audio transmissions simultaneously
- Web conferencing - blends audio, video, and document-sharing technologies to create virtual meeting rooms where people "gather" at a password-protected Web site
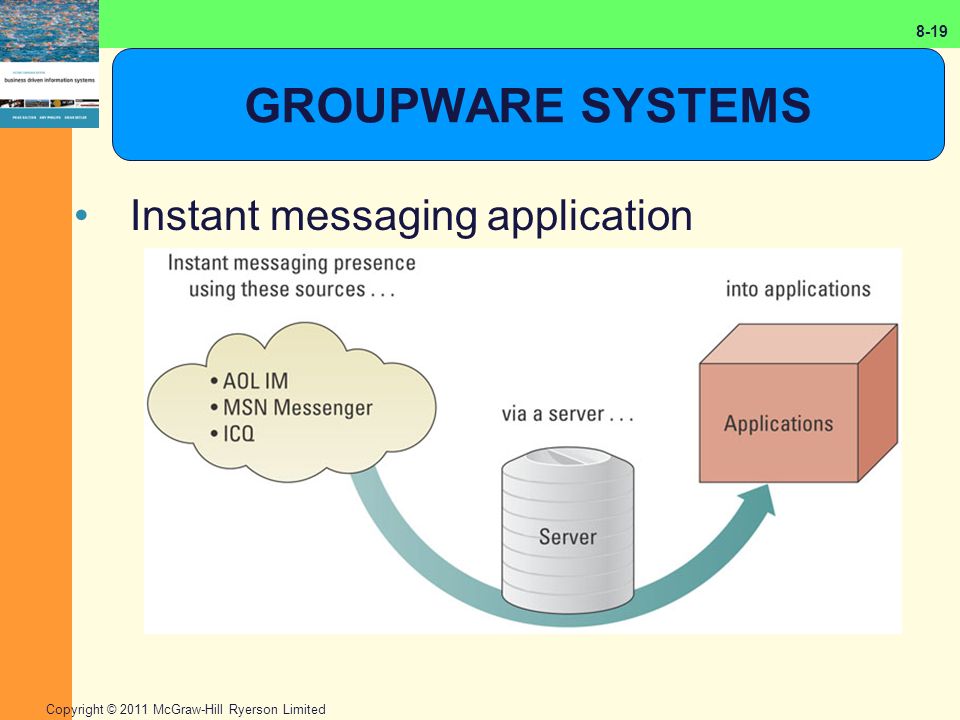
Instant Messaging:
- e-mail is the dominant from of collaboration application, but real-time collaboration tools like instant messaging are creating new communication dynamic
- instant messaging - type of communications services that enables someone to create a kind of private chat room with another individual to communicate in real-time over the internet
FRIDAY
15 DECEMBER 2017
Comments
Post a Comment