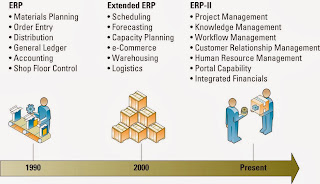
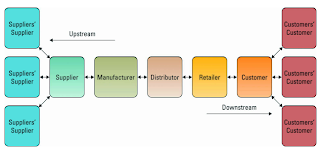
CHAPTER 15: OUTSOURCING
Outsourcing Outsourcing Projects: insourcing (in-house-development) - a common approach using the professional expertise within an organization to develop and maintain the organization's information technology systems outsourcing - an arrangement by which one organization provides a service or services for another organization that chooses not to perform them in-house onshore outsourcing - engaging another company within the same country for services nearshore outsourcing - contracting an outsourcing arrangement with a company in a nearby country offshore outsourcing - using organizations from developing countries to write code and develop systems big selling point for offshore outsourcing "inexpensive good work" factors driving outsourcing growth include: core competencies many companies have recently begun to consider outsourcing as a means to fuel revenue growth rather than just a cost-cutting measure financial savings it is typically