Chapter 3: STRATEGIC INTIATIVES FOR IMPLEMENTING COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGES
Strategic Intiatives For Implementing Competitive Advantages
- organizations can undertake high-profile strategic initiatives including:
- supply chain management (SCM)
- customer relationship management (CRM)
- business process reengineering (BPR)
- enterprise resource planning (ERP)
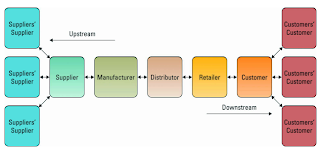
- Supply Chain Management (SCM)
- involves the management of information flows between and among stages in a supply chain to maximize total supply chain effectiveness and profitability
- four basic components of supply chain management include:
- Supply chain strategy- strategy for managing all resources to meet customer demand
- Supply chain partner- partner throughout the supply chain that deliver finished products, raw materials, and services.
- Supply chain operation- schedule for production activities
- Supply chain logistics- product delivery process
- Effective and efficient SCM systems can enable an organizaion to:
- decrease the power of its buyers
- increase its own supplier power
- increase switching costs to reduce the threat of substitute products or services
- create entry barriers thereby reducing the threat of new entrants
- increase efficiencies while seeking a competitive advantage through cost leadership
- Effective and efficient SCM systems effect on Porter's Five Forces
- Customer relationship management (CRM)
- involves managing all aspects of a customer's relationship with an organization to increase customer loyalty and retention and an organization's profitability
- many organizations, such as Charles Schwab and Kaiser Permanente, have obtained great success through theimplementation of CRM systems
- CRM is not just technology, but a strategy, process, and business goal that an organization must embrace on an enterprisewide level
- CRM can enable an rganization to:
- identify types of customers
- design individual customer marketing campaigns
- treat each customer as an individual
- understand customer buying behaviors
- Business process- a standardized set of activities that accomplish a specific task, such as processing a customer's order
- Business process reengineering (BPR)- the analysis and redesign of workflow within and between enterprises
- the purpose of BPR is to make all business processes best-in-class
- Reengineering the Corporation- book written by Michael Hammer and James Champy that recommends seven principles for BPR
- Finding Opportunity Using BPR
- a company can improve the way it travels the road by moving from foot to horse and then horse to car
- BPR looks at taking a different path, such as airplane which ignore the road completely
- progressive insurance mobile claims process
- type sof change an organization can achieve, along with the magnitudes of change and the potential business benefit
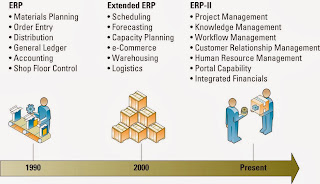
- Enterprise resource planning (ERP)
- integrates all departments and functions throughout an organization into a single IT system so that employees can make decisions by viewing enterprisewide information on all business operations.
- keyword in ERP is "enterprise"
- sample data from a sales database
- sample data from an accounting database
- ERP systems collect data from across an organization and correlates the data generating an enterprisewide view
5/10/2017
THURSDAY
Comments
Post a Comment